
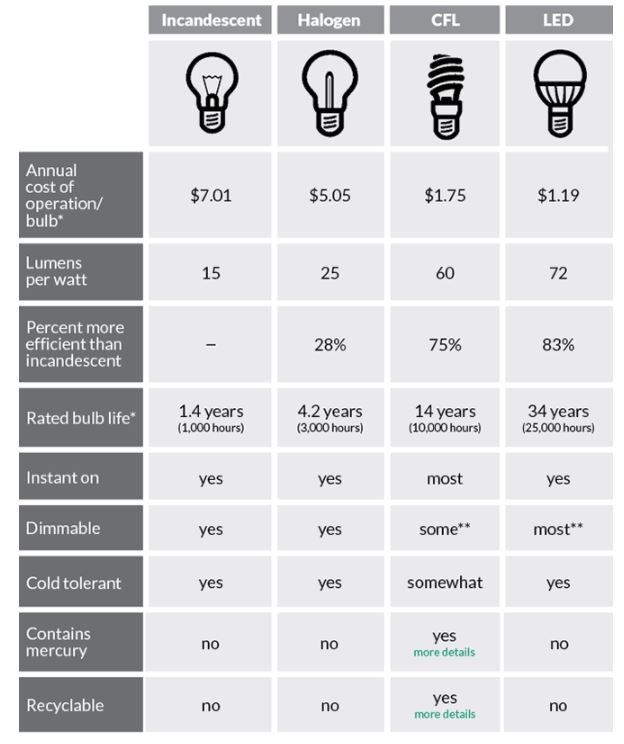
We have historically thought of the wattage of the bulb as being the main measure of its brightness but, with LED bulbs, technological improvements mean that the same level of light can be generated more energy-efficiently over time. The generally rule of thumb is to multiply the number of watts of an LED bulb by ten to get the approximate wattage for a traditional bulb It is important to remember that this is just a rule of thumb guide. What is the equivalent halogen wattage for LED bulbs? Where large numbers of lights are required, working in proximity to LED bulbs is a lot cooler than working around halogen bulbs They can be handled without the risk of burns, they are less likely to shatter & they are less likely to cause fires. Reduced heat generation - because they do not reply on the heating of an element, LED bulbs do not generate as much heat.The colour range - LEDs offer a wider range of lighting colour temperatures (this means that a range of electronic light can be produced to fit all requirements (such as providing an extremely bright light, an equivalent to daylight as well as cooler & whiter shades.LEDs are simple diodes (a single semiconductor). The technology - halogen lights are traditional bulbs (containing a tungsten filament in a halogen-gas filled-bulb).There are a number of differences between LED & halogen light bulbs. What is the difference between LED and halogen light bulbs? This reliability means that they are more useful for environments where a consistent level of light is required or where people are working with colour Instant light - as LED bulbs do not rely on the heating up of an element, they light up immediately, providing an instant & consistent level of light.LEDs are also less fragile & are shock & vibration-proof which lends them to more applications Increased versatility - because they do not generate as much heat & can be designed to give different levels of warmth & colour, LEDs are more versatile & can be used or configured for more varying situations.A typical halogen light may have a lifespan of 2,000 hours whereas LED bulbs could be expected to last 30,000 to 50,000 hours Increased reliability - LEDs are typically an order of magnitude more reliable than halogen bulbs.LED bulbs can also change colour, helping to make environments more exciting & interesting Increased variety - LED bulbs offer a range of options to suit different environments including different levels of warmth, brightness & beam angle.Reduced heat - LED bulbs typically emit a fraction of the heat of halogen bulbs (because of the technology used & because the resultant bulb is more energy-efficient.Scaled-up, the difference between all UK households using LED bulbs & halogen bulbs is a reduction in CO2 by 1.76 million tonnes Reduced environmental impact - a like-for-like brightness replacement of a halogen bulb for an LED bulb would save 5kg of CO2 emissions per year.Typically speaking, each LED lights will save £2 - £3 per year when compared to halogen. In the UK, lighting is around 15% of an average home energy bill. If LED lights use less energy, that means that you spend less on electricity. Cost savings - following on from energy savings are cost savings.This has a number of benefits, including a lower heat output & a significantly reduced impact on the environment. Energy efficiency- LED lights use a fraction of the energy of their halogen siblings.There are a number of advantages to LED lights over halogen. Manufacturers are required to list both the lumens produced as well as the watts used by every bulb, so luminous efficiency can be calculated easily (see References 5 and 6).In this article we will compare LED, Incandescent, Halogen, CFL and Fluorescent Light Bulbs. For example: It takes an incandescent bulb 60 watts to produce the same amount of light that would take a CFL bulb only 15 watts to produce (see References 2). Another element to look at is the watts it takes to produce the same amount of light. Luminous efficiency is one way to determine which bulb to choose, yielding CFLs as the most efficient, followed by halogen bulbs and then incandescent bulbs. The luminous efficiency of halogen lamps cradles between the previous two at an approximate 3.5 percent efficiency. The luminous efficiency of fluorescent lighting is the highest, between 9 percent and 11 percent for most CFLs, while conventional incandescent bulbs stand between 1.9 percent and 2.6 percent efficiency (see References 1). For a source of light to be 100 percent efficient, it would hypothetically need to give 680 lumens per watt (see References 1). Light is measured in units called "lumens," which correspond to the amount of light produced per watt.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
